American women have a one in eight chance (12.9%) of developing breast cancer during their lifetimes, while American men have a one in 800 chance (0.13%), according to the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute.
Each year, about 264,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer, and approximately 42,000 women die from the disease, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports. About 2,400 men are diagnosed with breast cancer each year and some 500 men die from it annually, CDC data shows.
Since breast cancer is more commonly found in women ages 40 and older, medical professionals and organizations recommend routine breast cancer screenings for middle-aged and senior women.
KATIE COURIC’S BREAST CANCER: WHAT OTHER WOMEN CAN LEARN FROM HER DIAGNOSIS
This includes mammograms — a breast cancer screening method that has led to age-based debates among experts.
There are several important breast cancer risk factors to note, say experts.
Medical professionals and organizations recommend routine breast cancer screenings for middle-aged and senior women. (iStock)
“Having one first-degree relative with breast cancer doubles a woman’s risk,” Dr. Kathleen Kiernan Harnden, director of breast oncology at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute in Annandale, Virginia, told Fox News Digital.
Other high-risk factors include a family history of breast cancer, a known genetic mutation or a previous breast biopsy, according to Harnden.
BREAST CANCER SURVIVOR’S INCLUSIVE LINGERIE BRAND CATERS TO DIAGNOSED WOMEN
Given this, Harnden said there are three questions all women should ask themselves before they request a mammogram consultation or appointment:
- Do I have an increased risk of breast cancer?
- How can I reduce my risk for breast cancer?
- Will my mammogram be three-dimensional (3D) or two-dimensional (2D)?
Harnden recommends 3D mammography over 2D because multiple images are taken from different angles, which may make breast tissue analysis clearer.
Here’s a deeper dive into these topics.
What is breast cancer?

About one in eight women will develop breast cancer in their lifetime, according to the National Cancer Institute. (iStock)
Breast cancer is a disease that occurs in breast tissue when cells in the breast “change and grow out of control,” according to MedlinePlus, an online health information service produced by the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
The cells that cause breast cancer usually form a tumor — an abnormal mass of tissue.
Cancer cells and cancerous tumors (malignant) are dangerous because they can disrupt organ functions and kill healthy cells if left to spread.
This can cause serious harm or death if left untreated, according to a report from MedicalNewsToday, a medical news website owned by Healthline Media.
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women after skin cancer, says the National Cancer Institute.
Female breast cancer rates by age group: CDC
- 15 to 19: 0.2 per 100,000 women
- 20 to 24: 1.8 per 100,000 women
- 25 to 29: 10.5 per 100,000 women
- 30 to 34: 30.1 per 100,000 women
- 35 to 39: 64.8 per 100,000 women
- 40 to 44: 131.7 per 100,000 women
- 45 to 49: 201 per 100,000 women
- 50 to 54: 240.7 per 100,000 women
- 55 to 59: 273.3 per 100,000 women
- 60 to 64: 339.8 per 100,000 women
- 65 to 69: 425.2 per 100,000 women
- 70 to 74: 475.8 per 100,000 women
- 75 to 79: 466.1 per 100,000 women
- 80 to 84: 420.7 per 100,000 women
- 85+: 318.2 per 100,000 women
Breast cancer diagnoses are extremely rare in teenagers. Teen girls between ages 15 and 19 have an incidence rate of 0.2 per 100,000, the CDC indicates.
Girls younger than 15 do not have a calculated breast cancer incidence rate because the CDC suppresses data when there are fewer than 16 cases, which the agency notes on its “United States Cancer Statistics: Data Visualizations” webpage.
Breast cancer incidence rates steadily increase with age, but it remains low for women under the age of 40, CDC data shows.
While not all experts agree on whether women under age 40 should receive mammograms, young women in their 20s and 30s have been diagnosed with breast cancer, according to incidence data published by the CDC, which dates back to 2019.
The incidence rate of breast cancer for middle-aged women steadily increases every four years.
Women between the ages of 20 and 24 have a breast cancer incidence rate of 1.8 per 100,000.
The incidence rate jumps to 10.5 per 1000,000 women, 30.1 per 100,000 women and 64.8 per 100,000 women, for women ages 25 to 29, 30 to 34 and 35 to 39, respectively.
WOMEN IN CONGRESS SPEAK OUT ABOUT EXPANDING ACCESS TO BREAST CANCER EXAMS
Breast cancer incidence rates spike from ages 40 to 74, the CDC’s data shows.
The incidence rate for middle-aged women steadily increases every four years. For example, women ages 40 to 44 have a breast cancer incidence rate of 131.7 per 100,000 women while women ages 55 to 59 have a breast cancer incidence rate of 273.3 per 100,000 women.
Breast cancer diagnoses are even more common in senior women. The CDC’s data shows women from age 60 to 64 have a breast cancer incidence rate of 339.8 per 100,000 women. Women from age 65 to 69 have a breast cancer incidence rate of 425.2 per 100,000 women. Women from age 70 to 74 have a breast cancer incidence rate of 475.8 per 100,000 women — the highest of any age group.
Declines in breast cancer incidence rates start to happen after age 75, according to the CDC.
What is a mammogram?
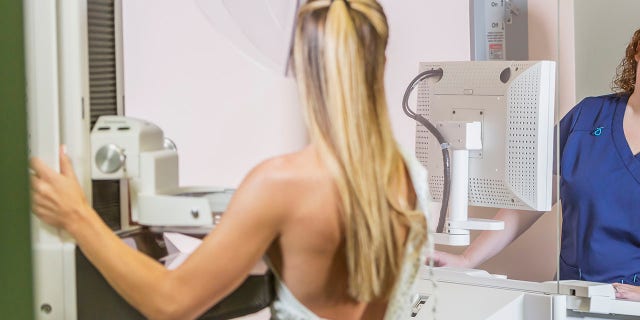
Mammography is a common breast cancer screening method that uses radiation to detect physical abnormalities in breast tissue. (iStock)
Mammograms are an X-ray procedure that helps doctors detect early signs of breast cancer, according to the CDC.
The machines used to conduct mammograms have plastic plates that flatten breasts, so X-ray images can be taken and analyzed by radiologists for abnormalities.
Mammogram results are typically reported in a few weeks, according to the CDC.
BREAST CANCER SYMPTOMS TO LOOK OUT FOR
Women with dense breasts have a higher chance of getting breast cancer, the health agency reports. Some women have higher-density breasts if they’re younger in age, pregnant or breastfeeding, taking hormone replacement therapy or have a lower body weight.
“Dense tissue can hide cancers,” the CDC wrote in a “What Does It Mean to Have Dense Breasts?” report.
“Fibrous and glandular tissue looks white on a mammogram. So does a possible tumor,” the CDC continued. “Because it’s hard to tell the difference between a tumor and dense breast tissue on a mammogram, a small tumor may be missed.”

Mammograms use X-ray imaging to detect breast cancer. (iStock)
Dr. Mona Jhaveri, cancer researcher and founder of Music Beats Cancer, a creative nonprofit organization in Washington, D.C., told Fox News Digital that dense breast tissue occurs in half of all women ages 40 and up.
“It’s well known that detecting cancer lesions in women with dense breast tissue can be difficult,” Jhaveri said. “Mammography is the standard of care for breast cancer screening, [but] it certainly has its risks and limitations.”
Delaying a breast cancer diagnosis has a higher risk than radiation exposure.
Potential risks associated with mammography screening include over diagnosis, false positives, anxiety and radiation injury, according to a study published in the National Library of Medicine.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force — an independent, volunteer panel of national experts in disease prevention — says women who place a higher value on the potential benefit of mammography over potential harm can choose to begin breast cancer screening once every two years between ages 40 and 49 years.
MELISSA ETHERIDGE RECALLS OLIVIA NEWTON-JOHN’S SUPPORT DURING HER OWN BATTLE AGAINST BREAST CANCER
The CDC says similar breast screening guidelines have been issued to women ages 40 to 49 with “average risk” by the American Cancer Society, American College of Physicians, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Radiology, American College of Physicians and American Academy of Family Physicians.

Some mammogram machines produce 2D images, while some produce 3D images. (iStock)
Three out of the six aforementioned cancer organizations recommend annual mammograms for concerned women who are between the ages of 40 and 49, if they so choose.
Women who are age 50 and older are generally advised to get mammograms done annually or bi-annually.
All cancer organizations advise women to speak with a health care provider to weigh the potential benefits and risks of getting a mammogram.
Age and family history of cancer are two factors that are taken into consideration during mammogram consultations, the CDC reports.
What should you know about mammogram radiation?
Dr. Jessica Shepherd, a Dallas-based OB-GYN who is chief medical officer at Verywell Health, a health information website, said most breast cancer cases are diagnosed after age 50, which is why mammograms are usually done for women who are closer to that age marker.
“The dose of radiation from a mammogram is pretty low and very rarely poses a risk, making them a safe diagnostic tool, and typically someone only needs a mammogram once a year. Therefore, there is no risk of too much radiation exposure,” Shepherd told Fox News Digital.
EXERCISE LOWERS THE RISK OF BREAST CANCER, STUDIES SHOW
She noted that there is a “small link to an increased risk of breast cancer over time due to [mammogram] frequency and also size of the breasts,” but “overall this increase in risk is very small.”
Delaying a breast cancer diagnosis has a higher risk than radiation exposure, Shepherd said.
“When caught early, breast cancer is highly treatable, and mammograms can be highly beneficial in these cases,” Shepherd continued. “If [breast cancer is] allowed to advance, a patient may have to receive more complex treatment such as surgery or chemo, which is way more invasive than radiation exposure from a mammogram.”
Breast cancer screening alternatives
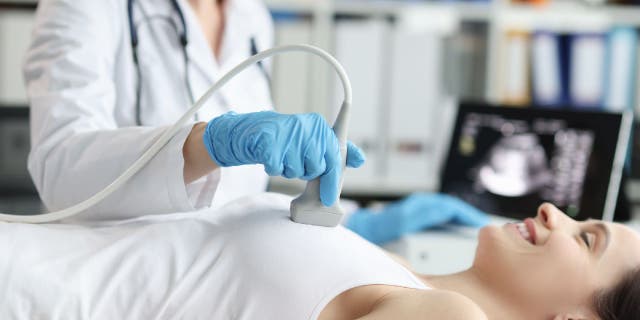
Breast ultrasound examinations can be done to diagnose potential breast tumors. (iStock)
Other breast cancer screening methods exist for women who are not eligible or do not want to undergo a mammogram.
The CDC lists breast ultrasounds, breast MRI clinical breast examinations and self-checks as possible screenings for breast cancer.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Ultrasounds generate pictures, or sonograms, using sound waves while MRIs are computerized body scans that generate pictures using magnets.
Clinical breast exams are conducted by a doctor or nurse. During exams, medical professionals check for abnormal lumps or other physically detectable changes in breast tissue by hand.
Women can check their breasts for common breast cancer symptoms, including lumps, pain and changes in size.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“You should report any changes that you notice to your doctor or health care provider,” the CDC wrote in a “What Is Breast Cancer Screening?” guide.
“Having a clinical breast exam or doing a breast self-exam has not been found to lower the risk of dying from breast cancer,” the CDC also said.
Ashlyn Messier of Fox News Digital contributed reporting.